Tariffs create price uncertainty for international shopping bag traders, which leads to unstable costs, lower profit margins, and unpredictable demand trends.
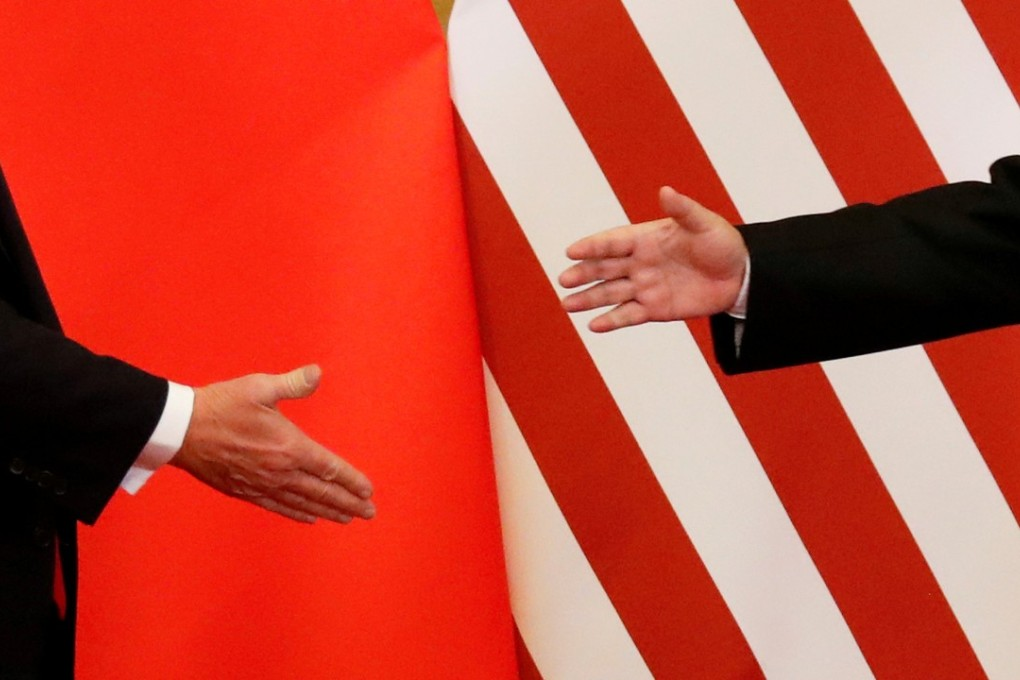
**Tariffs influence global shopping bag trade1 by raising costs, shifting supplier choices, disrupting logistics, and reducing demand due to increased retail prices.
If you deal with global shopping bag imports or exports2, understanding how tariffs work is essential to planning and profits.
What is the impact of tariffs on world trade?
Tariffs make international trade more expensive, especially for standardized products like shopping bags, where price competition is fierce.
Tariffs increase transaction costs and discourage global exchange, often leading to reduced trade volumes and rerouted supply chains.
When I first entered the international handbag market, I discovered that even a 5% tariff hike could erase most of my margins on a large shipment. This forced me to rethink my supplier network. As I explored deeper, I realized this is a common problem in global trade.
The World Trade Organization's View
| Aspect | Effect of Tariffs |
|---|---|
| Global Trade Volume | Decreases as tariffs increase |
| Price Competition | Weakens due to artificial cost inflation |
| Market Efficiency | Distorted as buyers avoid high-tariff markets |
| Supply Chain Choice | Suppliers shift to low-tariff countries |
Tariffs reduce the efficiency of global resource allocation. Countries impose them to protect local industries, but they often lead to supply chain reconfiguration. For example, if Ukraine raises tariffs on Chinese bags, traders like Nana might shift to Vietnam or Thailand, where duties are lower. Over time, this change alters trade patterns worldwide.
What happens when a country imposes a tariff on imports?
Import tariffs inflate the final price of foreign shopping bags, causing buyers to look for alternatives or buy less.
When import tariffs increase, import volumes usually drop, prices rise for end users, and domestic producers gain temporary price advantages.

A few years ago, I was preparing to ship a large batch of non-woven bags to Europe. Suddenly, the EU announced a temporary 10% import duty. Our European clients immediately froze their orders. Some tried to renegotiate prices. Others shifted to local suppliers despite their higher baseline costs.
Case Study: Tariff Shock Response
| Response Type | Example |
|---|---|
| Supplier Relocation | Moved orders from China to Vietnam |
| Order Cancellation | Buyers delayed or canceled confirmed orders |
| Cost Reallocation | Added tariff costs to wholesale prices |
| Buyer Adaptation | Sought cheaper packaging alternatives |
When a country imposes new tariffs, it causes an immediate shock to the trading environment. Importers must adapt quickly or risk loss. In my case, I split production between tariff-friendly markets and non-affected regions to stay competitive. It taught me the value of flexible supply networks.
What are the effects of export tariffs?
Export tariffs discourage producers from selling abroad by cutting their profits, which can shrink a country's global market share.
Export tariffs decrease outbound shipment volumes, raise domestic supply, and often trigger retaliatory actions from trade partners.

In 2021, I heard that India briefly considered taxing certain plastic-based packaging exports. That news alone made one of our partners in Japan pause negotiations. Export tariffs affect trust and reliability in business relationships. Even if not implemented, the rumor of them creates fear and hesitation.
How Export Tariffs Shift Market Behavior
| Market Response | Consequence |
|---|---|
| Exporter Reaction | Lower production or divert to local markets |
| Buyer Reaction | Seek alternative countries without tariffs |
| Price Reaction | Drop in export revenue; local prices may fall |
| Global Reaction | Trade partners may impose countermeasures |
Countries rarely use export tariffs on low-margin products like shopping bags unless they're in a resource or environmental crisis. Still, even discussions of such policies shake up supplier confidence. Exporters must monitor both domestic policies and overseas responses closely.
How do tariffs impact supply and demand?
Tariffs distort natural supply and demand by adding artificial costs, which shifts buyer and seller behaviors across borders.
Tariffs reduce demand for imported goods and boost local production, but they often lead to higher retail prices and inefficiencies.

When Canada increased tariffs on reusable plastic bags in 2020, one of my largest clients there halved their imports from Asia. They switched to a small domestic manufacturer. But within months, their shelves were emptier, and customer complaints rose. Local suppliers couldn’t scale up fast enough.
Tariff Impact on Market Dynamics
| Factor | Pre-Tariff Behavior | Post-Tariff Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Demand | Stable and predictable | Decreased for foreign bags |
| Supply | Global and diversified | Domestic-focused, limited scalability |
| Prices | Competitive and low | Higher due to tariff burden |
| Buyer Preferences | Quality and price-driven | Risk-averse, favoring policy stability |
Tariffs may help short-term local suppliers3, but in the long run, they reduce options and drive up costs for everyone. As a supplier, I always assess the demand elasticity of each market4—if prices rise 10%, will buyers drop orders or stay loyal?
Conclusion
Tariffs reshape global shopping bag trade by inflating costs, disrupting supply chains, and altering buyer behavior across borders.
-
Understand how tariffs impact pricing, sourcing, and trade flow in the global shopping bag market. ↩
-
Learn key tariff considerations for shopping bag businesses to avoid profit loss. ↩
-
Learn how local suppliers may temporarily gain from tariff protections. ↩
-
Understand how to forecast buyer behavior under different price scenarios ↩









